Neither Kareem nor I are much for starting conversations. We’re more the responder type so the poker hands we dealt went pretty quickly. Cathleen had a topic, though. “Speaking of black holes and polarized radio waves, I just read a paper claiming to have developed a 3‑dimensional movie of an event wider than Mercury’s orbit, all from the flickering of a single pixel.”
Eddie bets big, for him. Ten chips. “That’s a lot to ask from just a dot. And what’s polarization got to do with it?”
Cal folds but pipes up anyway. “What was the event?”
“You know Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole in the middle of our galaxy?”
“Yeah, one of those orange‑ring pictures.”
“Mm‑hm. Based on radio‑wave emissions from its accretion disk. That image came from a 2‑day Event Horizon Telescope study in 2017. Well, four days after that data was taken, the Chandra satellite observatory saw an X‑ray flare from the same region. The ALMA radio telescope team immediately checked the location. ALMA has excellent signal‑to‑noise and time‑resolution capabilities but it’s only one observatory, not world‑wide like the EHT. The EHT can resolve objects a hundred thousand times closer together than ALMA’s limit. But the team did a lot with what they had.”
Vinnie tends to bet big, maybe because he’s always skeptical. Fifteen chips. “You said ‘claiming‘ like there’s doubt. People don’t trust the data?”
“In science there’s always doubt. In this case, no‑one doubts the data — ALMA’s been providing good observations for over a decade. The doubt’s in the completely new AI‑driven data reduction technique the team used. Is what they did valid? Could their results have been affected by a ‘hallucination’ bug?”
Vinnie doesn’t let go. “What did they do, what have people been doing, and what’s hallucination?”
Susan reluctantly shoves fifteen chips into the pot. “Hallucination is an AI making up stuff. I just encountered that in a paper I’m reviewing. There’s a long paragraph that starts off okay but midway it goes off on a tangent quoting numbers that aren’t in the data. I don’t believe the submitting authors even read what they sent in.”
Kareem drops out of the betting but stays in the conversation. “For a lot of science, curve‑fitting’s a standard practice. You optimize a model’s parameters against measured data. X‑ray crystallography, for example. The atoms in a good crystal are arranged in a regular lattice, right? We send a narrow beam of X‑rays at the crystal and record the intensity reflected at hundreds of angles by the atoms in different lattice planes. Inside the computer we build a parameterized model of the crystal where the parameters are the x‑, y‑ and z‑coordinates of each atom. We have computer routines that convert a given set of configuration parameters into predicted reflection intensity at each observation angle. Curve‑fitting programs cycle through the routines, adjusting parameters until the predictions match the experimental data. The final parameter values give us the atomic structure of the crystal.”
“There’s a lot of that in astrophysics and cosmology, too. This new AI technique stands that strategy on its head. The researchers started with well‑understood physics outside of the event horizon — hot rotating accretion disk, strong magnetic field mostly perpendicular to that, spacetime distortion thanks to General Relativity — and built 50,000 in‑computer examples of what that would look like from a distance.”
“Why so many?”
“The examples had to cover one or two supposed flares of different sizes and brightness at different points in their orbits, plus noise from the accretion disk’s radiation, all from a range of viewpoint angles. Mind you, each example’s only output was a single signal intensity and polarization angle (that’s two dimensions) for that specific set of disk and flare configuration parameters. The team used the example suite to train an AI specialized for assembling 2‑dimensional visual data into a 3‑dimensional model. The AI identified significant patterns in those 50,000 simulated signals. Then the team confronted the trained AI with 100 minutes of real single‑pixel data. It generated this…”
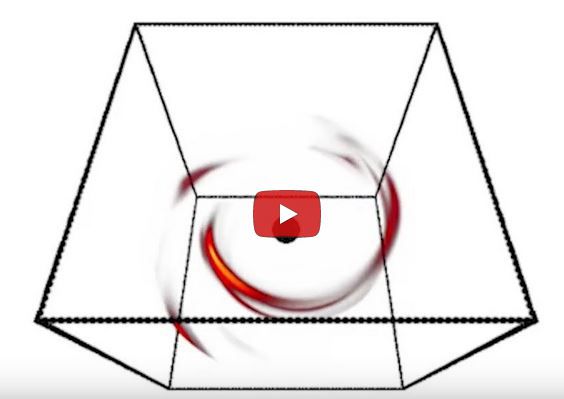
“Curve‑fitting but we don’t know the curves!”
“True, Sy, but the AI does.”
“Maybe.”
~ Rich Olcott
