I’ll be sorry when Acme Building’s management swaps out our old‑style door locks for electronic ones. Vinnie has such fun lock‑picking his way past my office door in the morning. “Morning, Vinnie.”
“Morning, Sy. Hey, I got a new Crazy Theory for you. Nobody knows what Dark Matter is, right?”
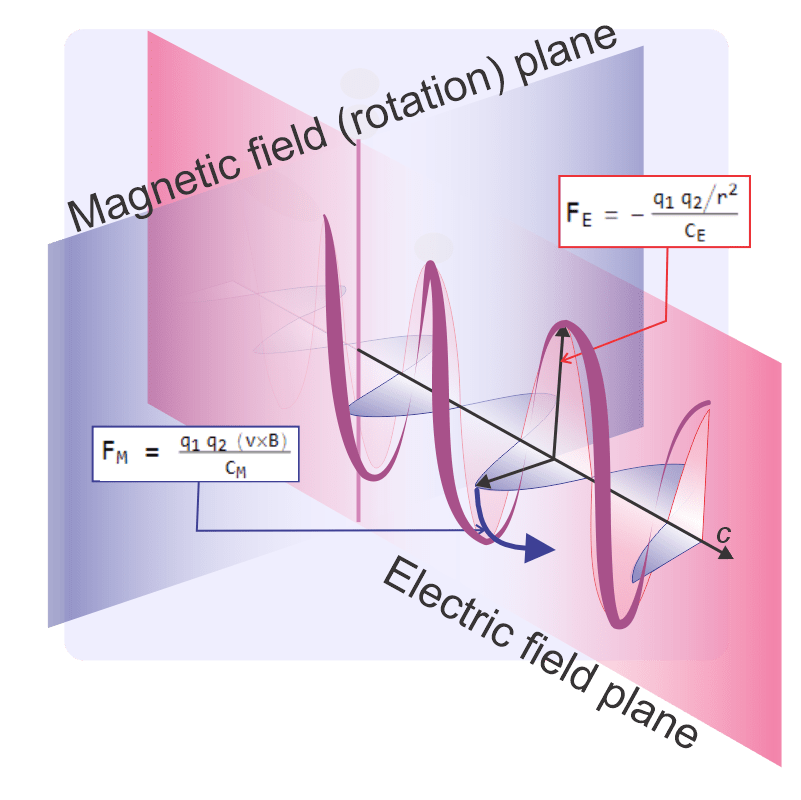
“Right. All we know is that it has about five times as much mass as normal matter so it participates in gravitational interactions. Some of it seems to gather in spherical halos around galaxies and some of it seems to collect in spikes near their centers. Cosmologists are arguing about whether or not Dark Matter is particles, much less how they’d be quantized. And we call it Dark because it absolutely doesn’t care about electromagnetism.”
“That’s what I thought. I remember you said if Dark Matter did play with light waves at all it’d block our view of the CMB. So yeah, absolute. Good.”
“I gather your theory is about Dark Matter.”
“Mm-hm. I thought of a way that all that mass could be hiding in plain sight except we can’t see it.”
“Alright, I’m listening.”
“Tachyons.”
“Come again?”
“Tachyons — particles that fly around faster than light. I read an article about ’em. Some people say they can’t exist but hear me out, okay? The reason they’re not supposed to exist is ’cause it would take an infinite amount of energy to boost something up past lightspeed. I got that, but suppose they were born above lightspeed, back when the Big Bang singularity had energy packed so tight the Physics laws we know don’t apply. A lot of particles got flung out below lightspeed, but maybe even more got flung out above it.”
“What does this have to do with dark matter?”
“I’m gettin’ there. The thing with tachyons is, the article said it’d take infinite energy to slow one down to lightspeed. A tachyon rock hits a slow rock, it don’t stop ’cause the slow rock don’t have the juice for that. The collision may take a little energy from the tachyon rock but that just changes its trajectory.”
“Mmm, those tachyon rocks can’t be a thing. The — what can I call it? slow matter?”
“The article called ’em bradyons.”
“Thanks. We know that 92% of all … bradyonic atoms in the Universe are hydrogens. Rocks are made of silicon, oxygen and other atoms that are even heavier. Everything heavier than hydrogen and maybe some helium was created by nuclear reactions inside a star. Tachyonic atoms zooming beyond lightspeed couldn’t gather together to form a star or even join one. No significant tachyonic fusion, no tachyonic rocks.”
“Okay, they all stay tachy‑hydrogen, still not a problem. The point is, there could be a lot of them and they could add up to a lot of mass. So the next thing I asked is, where would tachyons hang out? Gotta be around galaxies, but being tachyons going super‑lightspeed they can’t just hang, they orbit around the centers. They’d spend the most time where they go slowest which is where they’re farthest away ’cause that’s how orbits work. But they’d be thickest close in ’cause of gravity but that’s where they go fastest.”
“Cute, so you’re predicting galaxies with halos of tachyons, plus spikes of them at each center. That just happens to be the dark matter distribution the astronomers find.”
“It gets better, Sy. I’m not so sure of this because math, but it feels right. I don’t think tachyons can do electromagnetism things.”
“Why not?”
“No blue glow — you know, that blue glow in nuclear reactors when electrons go through the cooling water faster than light?”
“Cherenkov radiation, happens when fast electrons polarize the water. The polarizing slows light in water relative to a vacuum.”
“Right, but tachyons in space travel through vacuum. They ought to polarize the vacuum like what fast electrons do to water. Electromagnetic tachyons orbiting galaxies ought to make a blue glow but there isn’t one, so tachyons don’t do electromagnetism things and that makes them Dark Matter.”
“You’re going to have to do better than that, Vinnie. Absence of evidence just might be evidence of absence. Maybe they’re not there to begin with.”

~ Rich Olcott