<chirp, chirp> “Moire here.”
“Hello, Mr Moire. Remember me?”
“Yes, I do, Walt. I hope your people were satisfied with what you brought them from our last meeting.”
“They were, which is why I’m calling. Buy you pizza at Eddie’s, fifteen minutes?”
“Make it twenty.”
We’re at the rear‑corner table, Walt facing both doors, naturally. “So, what’s the mysterious question this time?”
“Word on the street is that the CPT Law’s being violated. We want to know who’s involved, and what’s their connection with ChatGPT.”
Good thing I’ve just bit into my pizza so I can muffle my chuckle in my chewing. “What do you know about anti‑matter?”
“Inside‑out atoms — protons outside whizzing around electrons in the nucleus.”
“Common misconception. One proton has the mass of 1800 electrons. An atom built as you described would be unstable — the thing would fly apart. You’ve got anti‑matter’s charges arranged right but not the particles. Anti‑matter has negative anti‑protons in the nucleus and positrons, positive electrons, on the outside.”
<writing rapidly in his notebook> “You can do that? Just flip the sign on a particle?”
“No, positrons and such are respectable particles in their own right, distinct from their anti‑partners. Electric charge comes built into the identity. What’s important is, an anti‑atom behaves exactly like a normal atom does. Maxwell’s Equations and everything derived from them, including quantum mechanics, work equally well for either charge structure.”
“There’s a bit of Zen there — change but no‑change.”
“Nice. Physicists call that sort of thing a symmetry. In this case it’s charge symmetry, often written as C.”
“The C in CPT?”
“Exactly.”
“What about the P and T?”
“When someone says something is symmetrical, what do you think of first?”
“Right side’s a reflection of left side. Symmetrical faces look better but they’re usually less memorable.”
“Interesting choice of example. Anyway, reflection symmetry is important in common physical systems.”
“Classical Greek and Cambodian architecture; the Baroque aesthetic without the decorative frills.”
“I suppose so. Anyway, we call reflection symmetry Parity, or P for short.”
“And T?”
“Time.”
“Time’s not symmetrical. It’s always past‑to‑future.”
“Maybe, maybe not. In all our physical laws that deal with a small number of particles, you can replace t for time with –t and get the same results except for maybe a flipped sign. Newton’s Laws would run the Solar System in reverse just as well as they do forward.”
“But … Ah, ‘small number of particles,’ that’s your out. If your system has a large number of particles, you’re in chaos territory where randomness and entropy have to increase. Entropy increase is the arrow for one‑way time.”
“Good quote.”
“I’ve been in some interesting conversations. You’re not my only Physics source. So CPT is about Charge AND Parity AND Time symmetries. But you can’t simply add them together.”
“You multiply them. Technically, each of them is represented by a mathematical operator—”
“Step away from the technically.”
“Understood. This’ll be simpler. If a system’s atoms have positive nuclei, set C=1, otherwise set C=–1. If the system’s naturally‑driven motion is counterclockwise set P=1, otherwise P=–1. If time is increasing, set T=1, otherwise set T=–1. Okay?”
“Go on.”
“You can summarize any system’s CPT state by multiplying the prevailing symmetry values. The product will be either +1 or –1. The CPT Law says that in any universe where quantum mechanics and relativity work, one CPT state must hold universe‑wide.”
“Make it real for me.”
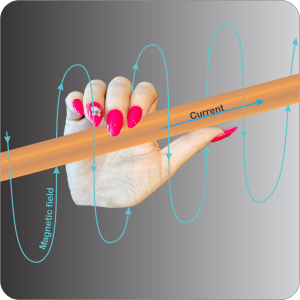
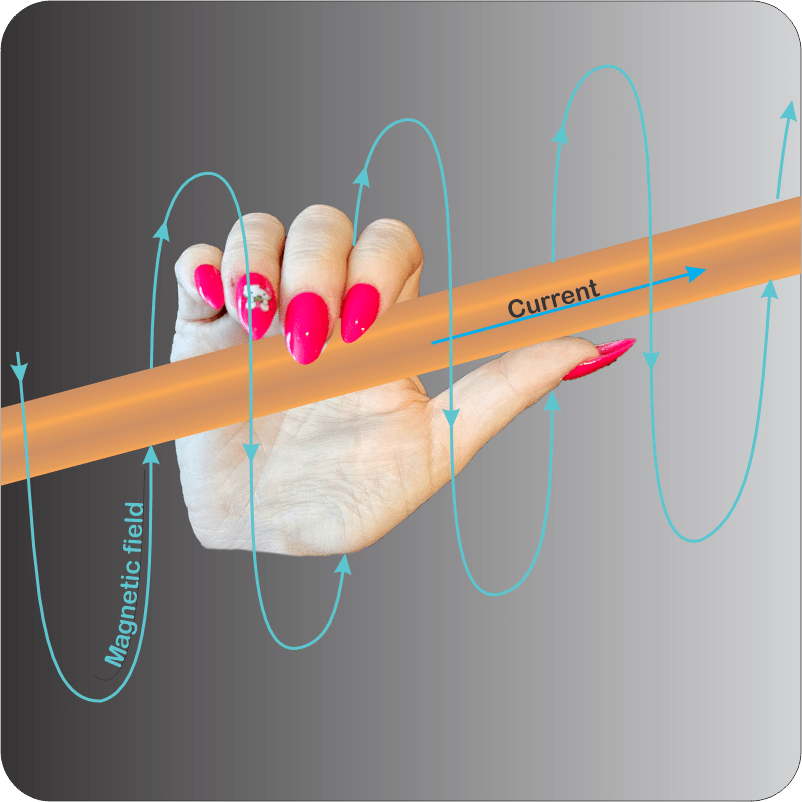
“You know the Right-hand Rule for electromagnetism?”
“Grab the wire with your right hand, thumb pointing along the current. Your fingers wrap in the direction of the spiraling magnetic field.”
“Perfect. Suppose C*P*T=+1 for this case. Now reverse the charge, making C=–1. What happens?”
“Ssss… The magnetic spin flips orientation. That’s a reflection operation so P=–1. The C*P*T calculation is (+1)*(–1)*(–1)=+1, no change.”
“The CPT Law in action. The CPT violation you’ve heard about is only observed in rare weak‑force‑mediated radioactive decays of a carefully prepared nucleus. That was a 1956 Nobel‑winning discovery, though the right person didn’t win it.”
“1956. Decades before A.I.”
“Yup, ChatGPT is off the hook. For that.”
“Bye.”
“Don’t mention it.”
~ Rich Olcott
- Thanks to Caitlin, the hand model.