There’s a commotion in front of Al’s coffee shop. Perennial antiestablishmentarian Change-me Charlie’s set up his argument table there and this time the ‘establishment’ he’s taking on is Astrophysics. Charlie’s an accomplished chain-yanker and he’s working it hard. “There’s no evidence for dark matter, they’ve never found any of the stuff and there’s tons of no-dark-matter theories to explain the evidence.”

Big Cap’n Mike’s shouts from the back of the crowd. “What they’ve been looking for and haven’t found is particles. By my theory dark matter’s an aspect of gravity which ain’t particles so there’s no particles for them to find.”
Astronomer-in-training Jim spouts off right in Charlie’s face. “Dude, you can’t have it both ways. Either there’s no evidence to theorize about, or there’s evidence.”
Physicist-in-training Newt Barnes takes the oppo chair. “So what exactly are we talking about here?”
“That’s the thing, guy, no-one knows. It’s like that song, ‘Last night I saw upon the stair / A little man who wasn’t there. / He wasn’t there again today. / Oh how I wish he’d go away.‘ It’s just buzzwords about a bogosity. Nothin’ there.”
I gotta have my joke. “Oh, it’s past nothing, it’s a negative.”

“Come again?”
“The Universe is loaded with large rotating but stable structures — solar systems, stellar binaries, globular star clusters, galaxies, galaxy clusters, whatever. Newton’s Law of Gravity accounts nicely for the stability of the smallest ones. Their angular momentum would send them flying apart if it weren’t for the gravitational attraction between each component and the mass of the rest. Things as big as galaxies and galaxy clusters are another matter. You can calculate from its spin rate how much mass a galaxy must have in order to keep an outlying star from flying away. Subtract that from the observed mass of stars and gas. You get a negative number. Something like five times more negative than the mass you can account for.”
“Negative mass?”
“Uh-uh, missing positive mass to combine with the observed mass to account for the gravitational attraction holding the structure together. Zwicky and Rubin gave us the initial object-tracking evidence but many other astronomers have added to that particular stack since then. According to the equations, the unobserved mass seems to form a spherical shell surrounding a galaxy.”
“How about black holes and rogue planets?”
Newt’s thing is cosmology so he catches that one. “No dice. The current relative amounts of hydrogen, helium and photons say that the total amount of normal matter (including black holes) in the Universe is nowhere near enough to make up the difference.”
“So maybe Newton’s Law of Gravity doesn’t work when you get to big distances.”
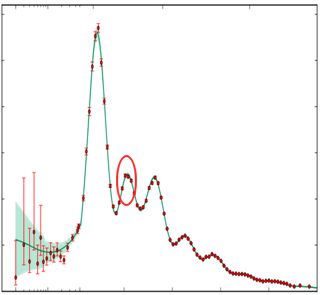
“Biggest distance we’ve got is the edge of the observable Universe. Jim, show him that chart of the angular power distribution in the Planck satellite data for the Cosmological Microwave Background.” <Jim pulls out his smart-phone, pulls up an image.> “See the circled peak? If there were no dark matter that peak would be a valley.”
Charlie’s beginning to wilt a little. “Ahh, that’s all theory.”

<Jim pulls up another picture.> “Nope, we’ve got several kinds of direct evidence now. The most famous one is this image of the Bullet Cluster, actually two clusters caught in the act of colliding head-on. High-energy particle-particle collisions emit X-rays that NASA’s Chandra satellite picked up. That’s marked in pink. But on either side of the pink you have these blue-marked regions where images of further-away galaxies are stretched and twisted. We’ve known for a century how mass bends light so we can figure from the distortions how much lensing mass there is and where it is. This picture does three things — it confirms the existence of invisible mass by demonstrating its effect, and it shows that invisible mass and visible mass are separate phenomena. I’ve got no pictures but I just read a paper about two galaxies that don’t seem to be associated with dark matter at all. They rotate just as Newton would’ve expected from their visible mass alone. No surprise, they’re also a lot less dense without that five-fold greater mass squeezing them in.”
“You said three.”
“Gotcha hooked, huh?
~~ Rich Olcott





 “Gravitational waves are relativity effects and neutrinos are quantum mechanical. Physicists have been struggling for a century to bridge those two domains. Evidence from a three-messenger event could provide the final clues.”
“Gravitational waves are relativity effects and neutrinos are quantum mechanical. Physicists have been struggling for a century to bridge those two domains. Evidence from a three-messenger event could provide the final clues.”


 “Half an eV? That’s all? So how come the Big Guy’s got gazillions of eV’s?”
“Half an eV? That’s all? So how come the Big Guy’s got gazillions of eV’s?” “That infinity sign at the bottom means ‘as big as you want.’ So to answer your first question, there isn’t a maximum neutrino energy. To make a more energetic neutrino, just goose it to go even closer to the speed of light.”
“That infinity sign at the bottom means ‘as big as you want.’ So to answer your first question, there isn’t a maximum neutrino energy. To make a more energetic neutrino, just goose it to go even closer to the speed of light.”



 “Thanks, Sy. Look, we’ve got three intervals where everything syncs up. See the new satellite peaks half-way in between? There’s more hidden pattern where things look chaotic in the rest of the space.”
“Thanks, Sy. Look, we’ve got three intervals where everything syncs up. See the new satellite peaks half-way in between? There’s more hidden pattern where things look chaotic in the rest of the space.”

 “Why should there be flashes? I thought neutrinos didn’t interact with matter.”
“Why should there be flashes? I thought neutrinos didn’t interact with matter.”

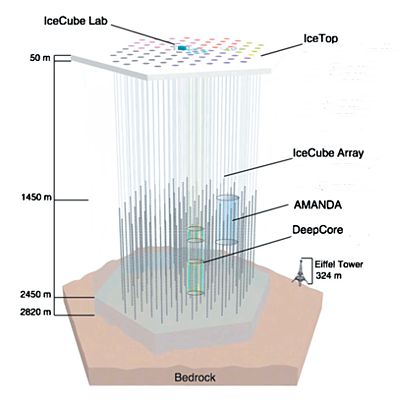
 Cathleen saves me from answering. “Not quite. The study Sy’s chasing is actually a cute variation on red-shift measurements. That ‘PSR‘ designation means the neutron star is a pulsar. Those things emit electromagnetic radiation pulses with astounding precision, generally regular within a few dozen nanoseconds. If we receive slowed-down pulses then the object’s going away; sped-up and it’s approaching, just like with red-shifting. The researchers derived orbital parameters for all three bodies from the between-pulse durations. The heavy dwarf is 200 times further out than the light one, for instance. Not an easy experiment, but it yielded an important result.”
Cathleen saves me from answering. “Not quite. The study Sy’s chasing is actually a cute variation on red-shift measurements. That ‘PSR‘ designation means the neutron star is a pulsar. Those things emit electromagnetic radiation pulses with astounding precision, generally regular within a few dozen nanoseconds. If we receive slowed-down pulses then the object’s going away; sped-up and it’s approaching, just like with red-shifting. The researchers derived orbital parameters for all three bodies from the between-pulse durations. The heavy dwarf is 200 times further out than the light one, for instance. Not an easy experiment, but it yielded an important result.”
 “OK,
“OK,