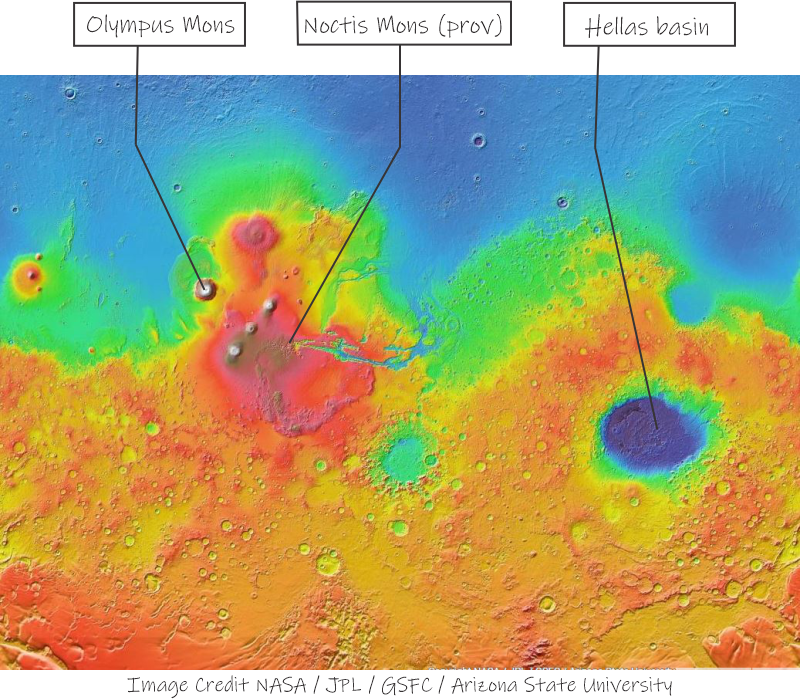
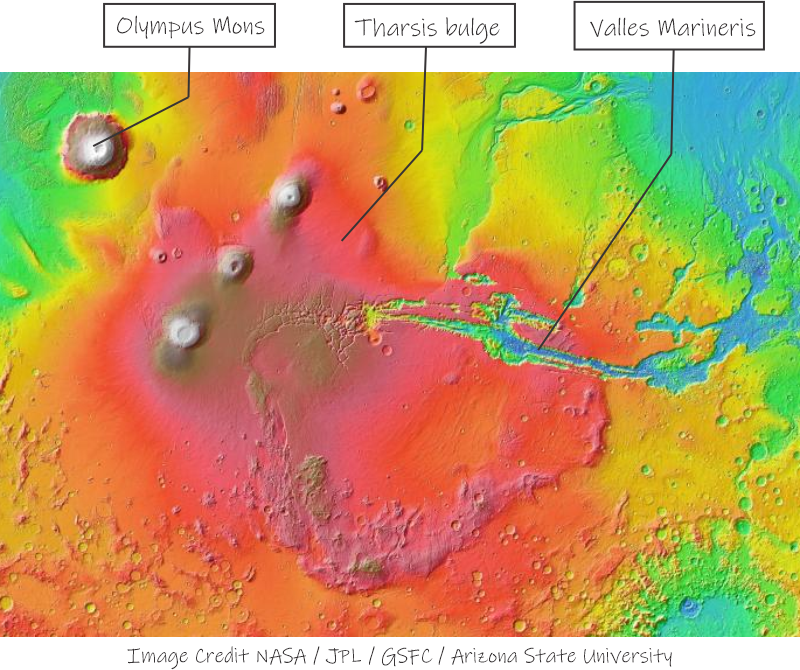
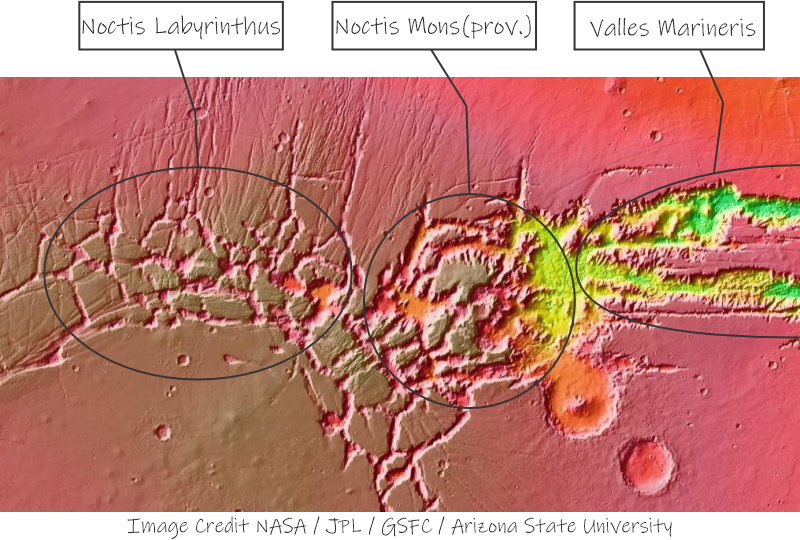
Particularly potent pepperoni on Pizza Eddie’s special tonight so I dash to the gelato stand. “Two dips of pistachio in a cup, please, Jeremy, and hurry. Hey, why the glum look?”
“The season’s moving so slowly, Mr Moire. I’m a desert kid, used to bright skies. I need sunlight! We’re getting just a few hours of cloudy daylight each day. It seems like we’re never gonna leave this pattern. Here’s your gelato.”
“Thanks. Sorry about the cloudiness, it’s the wintertime usual around here. But you’re right, we’re on a plateau.”
“Nosir, the Plateau’s the Four Corners area, on the other side of the Rockies, miles and miles away from here.”

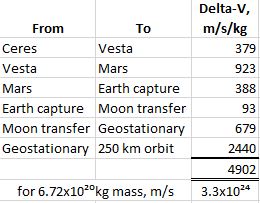
<chuckle> “Not the Colorado Plateau, the darkness plateau. Or the daylight trough, if you prefer. Buck up, we’ll get a daylight plateau starting in a few months.” <unholstering Old Reliable> “Here’s a plot of daylight hours through the year at various northern latitudes. We’re in between the red and green curves. For folks south of the Equator that’d just turn upside‑down, of course. I added a star at today’s date in mid‑December, see. We’re just shy of the winter solstice; the daylight hours are approaching the minimum. You’re feeling stressed because these curves don’t change much day-to-day near minimum or maximum. In a couple of weeks the curve will bend upwards again. Come the Spring equinox, you’ll be shocked at how rapidly the days lengthen.”
“Yeah, my Mom says I’m too impatient. She says that a lot. Okay, above the Arctic Circle they’ve got months‑long night and then months‑long day, I’ve read about that. I hadn’t realized it was a one‑day thing at the Circle. Hey, look at the straight lines leading up to and away from there. Is that the Summer solstice? Those low‑latitude curves look like sine waves. Are they?”
“Summer solstice in the northern hemisphere, Winter solstice for the southerners. The curves are distorted sines. Ready for a surprise?”
<Looks around the nearly empty eatery.> “With business this slow I’m just sitting here so I’m bored. Surprise me, please.”
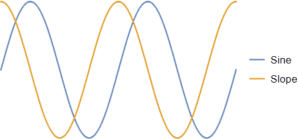
“Sure. One of the remarkable things about a sine wave is, when you graph its slopes you get another sine wave shifted back a quarter. Here, check it out.”
“Huh! When the sine wave’s mid-climb, the slope’s at its peak. When the sine wave’s peaking, the slope’s going through zero on the way down. And they do have exactly the same shape. I see where you’re going, Mr Miore. You’re gonna show me the slopes of the daylight graphs to see if they’re really sine waves.”
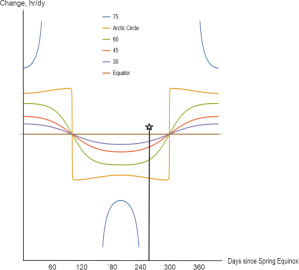
“You’re way ahead of me and Old Reliable, Jeremy.” <frantic tapping on OR’s screen> “There, point‑by‑point slopes for each of the graphs. Sorta sine‑ish near the Equator but look poleward.”
“The slopes get higher and flatter until the the Arctic Circle line suddenly drops down to flip its sign. Those verticals are the solstices, right?”
“Right. Notice that even at the Circle the between‑solstice slopes aren’t quite constant so the straight lines you eye‑balled aren’t quite that. North of the Circle the slopes go nuts because of the abrupt shifts between varying and constant sun.”
“How do you get these curves, Mr Moire?”
“It’s a series of formulas. Dust off your high school trig. The Solar Declination Angle equation is about the Sun’s height above or below the horizon. It depends on Earth’s year length, its axial tilt and the relative date, t=T‑T0. For these charts I set T0 to the Spring equinox. If the height’s negative the Sun’s below the horizon, okay?”
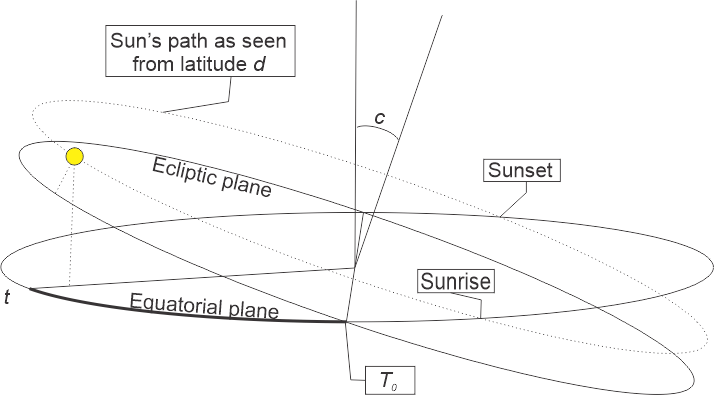
“Sine function is opposite‑over‑hypotenuse and the height’s opposite alright or we’d burn up, yup.”
“The second formula gives the the Hour Angle between your longitude and whichever longitude has the Sun at its zenith.”
“Why would you want that?”
“Because it’s the heart of the duration formula. When you roll all three formulas together you get one big expression that gives daylight duration in terms of Earth’s constants, time of year and your location. That’s what I plotted.”
“How about the slope curves?”
“Calculus, Jeremy, d/dt of that combined duration function. It’s beyond my capabilities but Old Reliable’s up to it.”

~ Rich Olcott