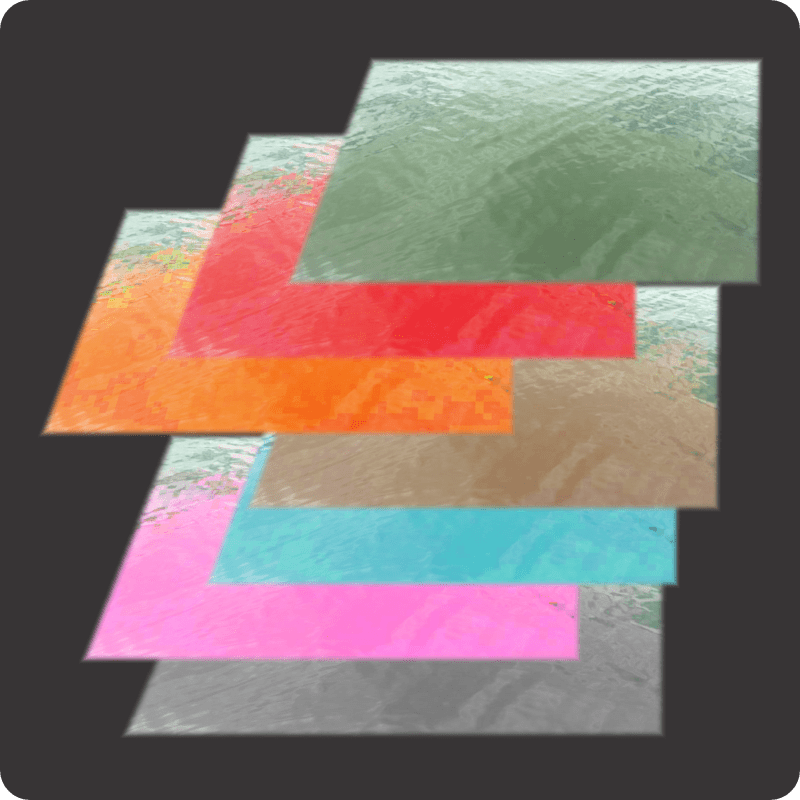“I guess I’m not surprised, Sy.”
“At what, Vinnie?”
“That quantum uses these imaginary numbers — sorry, you’d prefer we call them i‑numbers.”
“Makes no difference to me, Vinnie. Descartes’ pejorative term has been around for three centuries so that’s what the literature uses. It’s just that most people pick up the basic idea more quickly without the woo baggage that the real/imaginary nomenclature carries along. So, yes, it’s true that both i‑numbers and quantum mechanics appear mystical, but really quantum mechanics is the weird one. And relativity.”
“Wait, relativity too? That’s hard to imagine, HAW!”
“Were you in the room for Jim’s Open Mic session where he talked about Minkowski’s geometry?”
“Nope, missed that.”
“Ah, okay. Do you remember the formula for the diagonal of a rectangle?”
“That’d be the hypotenuse formula, c²=a²+b². Told you I was good at Geometry.”
“Let’s use ‘d‘ for distance, because we’re going to need ‘c‘ for the speed of light. While we’re at it, let’s replace your ‘a and ‘b‘ with ‘x‘ and ‘y,’ okay?”
“Sure, why not?”
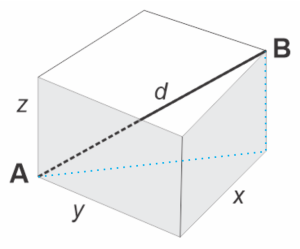
<casting image onto office monitor> “So the formula for the body diagonal of this box is…”
“Umm … That blue line across the bottom’s still √(x²+y²) and it’s part of another right triangle. d‘s gotta be the square root of x²+y²+z².”
“Great. Now for a fourth dimension, time, so call it ‘t.’ Say we’re going for light’s path between A at one moment and B some time t later.”
“Easy. Square root of x²+y²+z²+t².”
“That’s almost a good answer.”
“Almost?”
“The x, y and z are distance but t is a duration. The units are different so you can’t just add the numbers together. It’d be like adding apples to bicycles.”
“Distance is time times speed, so we multiply time by lightspeed to make distance traveled. The formula’s x²+y²+z²+(ct)². Better?”
“In Euclid’s or Newton’s world that’d be just fine. Not so much in our Universe where Einstein’s General Relativity sets the rules. Einstein or Minkowski, no‑one knows which one, realized that time is fundamentally perpendicular to space so it works by i‑numbers. You need to multiply t by ic.”
“But i²=–1 so that makes the formula x²+y²+z²–(ct)².”
“Which is Minkowski’s ‘interval‘ between an event at A and another event at B. Can’t do relativity work without using intervals and complex numbers.”
“Well that’s nice but we started talking about quantum. Where do your i‑numbers come into play there?”
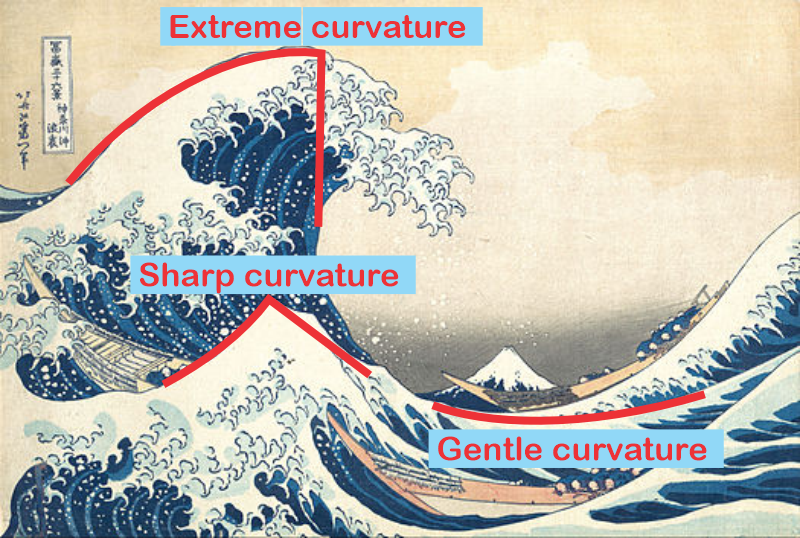
“It goes back to the wave equation— no, I know you hate equations. Visualize an ocean wave and think about describing its surface curvature.”
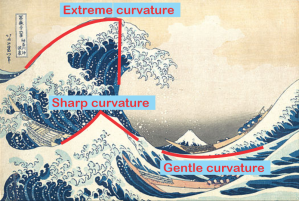
by Katsushika Hokusai, in public domain
“Curvature?”
“How abruptly the slope changes. If the surface is flat the slope is zero everywhere and the curvature is zero. Up near the peak the slope changes drastically within a short distance and we say the surface is highly curved. With me?”
“So far.”
“Good. Now, visualize the wave moving past you at some convenient speed. Does it make sense that the slope change per unit time is proportional to the curvature?”
“The pointier the wave segment, the faster its slope has to change. Yeah, makes sense.”

“Which is what the classical wave equation says — ‘time‑change is proportional to space‑change’. The quantum wave equation is fundamental to QM and has exactly the same form, except there’s an i in the proportionality constant and that changes how the waves work.” <casting a video> “The equation’s general solution has a complex exponential factor eix. At any point its value is a single complex number with two components. From the x‑direction, the circle looks like a sine wave. From the i‑direction it also looks like a sine wave, but out of phase with the x‑wave, okay?”
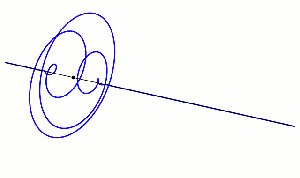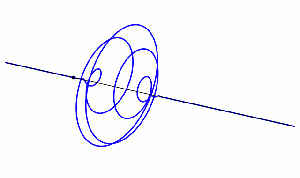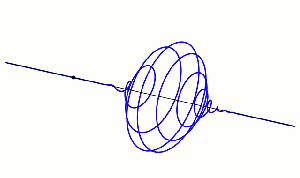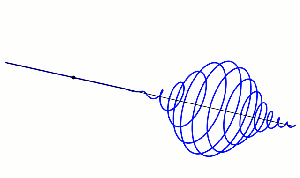
Image by “Xcodexif” under CCS-A 4.0 license
“Out of phase?”
“When one wave peaks, the other’s at zero and vice‑versa. The point is, rotation’s built into the quantum waves because of that i‑component.” <another video> “Here’s a lovely example — that black dot emits a photon that twists and releases the electromagnetic field as it moves along.”
~ Rich Olcott