A quiet morning at Cal’s Coffee. I’m sipping my morning mud when Susan Kim bustles to my table, mocha latte in hand. “There you are, Sy. I loved your posts in tribute to the well‑thumbed copy of the CRC Handbook on my desk.”
“Glad you enjoyed them.”
“Your Rumford stuff made it even better because I did a class report on him once so I caught your ‘frigorific‘ reference. What do you know about the background to that?”
“Not much. Didn’t sound like a real word when I ran across it.”
“Oh, it’s a real word but it has a technical meaning now that it didn’t in Newton’s time. Back then it was only about making something cold. These days we also use the word for a mixture that maintains a dependable cold temperature. Liquid water and ice, for instance, stays at 0°C as long as there’s still ice in the cold bath. I used to use an ammonium chloride/water frigorific when I needed something down around -15°C. Now of course I use a benchtop refrigerator.”
“Rumford would have liked that. What were the ‘frigorific rays‘ he got all excited about?”
“Long story but there’s a couple of fun twists. Background first. At the end of the 1700s there was a <grin> heated debate about heat. The phlogiston theory was dead by that time but people still liked the idea that heat was a material fluid. It addressed some chemical puzzles but heat transmission was still mysterious. Everyone knew that a hot object gives off heat by radiation, that the radiation travels in straight lines and that it’s reflected by metal mirrors.”
“Right, the Greeks are supposed to have used huge sun‑focusing mirrors to burn up attacking Roman ships.”
“Maybe. Anyhow, those properties connected heat with light. However, a pane of glass blocks radiated heat, at least until the glass gets hot. People argued this meant heat and light weren’t connected. About 1790 a group of physicists loosely associated with the Academy of Geneva dove into the fray. Rumford was in the group, along with Prévost, Saussure and his student Pictet. They had lots of fun with heat theories and experiments. One of Pictet’s experiments lit Rumford’s fire, so to speak.”
“Good one.”
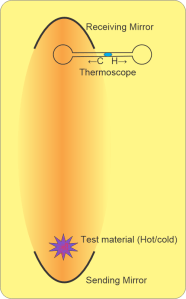
<smile> “It’s a fairly simple setup that a high school science teacher could do. Pictet hung a concave metallic mirror facing down from the ceiling of a draft‑free room. He placed another concave metallic mirror at floor level immediately beneath it, facing upward. He probably used spherical mirrors which are easy to make, but they could have been elliptical or parabolic sections. Anyhow, he put a thermoscope at the upper mirror’s focal point and a hot object at the lower focal point. Sure enough, the upper focal point got hotter, just as you’d expect.”
“No great surprise, the Greeks would have expected that, too.”
“The surprise happened when he put a cold object in there. The thermoscope’s droplet moved in the cold direction.”
“Wait, like anti‑infrared?”
“That’s the effect. Wave‑theory supporter Rumford took that thought, called it ‘frigorific radiation‘ and ran with it. He constructed a whole thesis around cold waves and heat waves as symmetric partners. He maintained wave intensity, both kinds, increases with temperature difference. Our heat sources are hundreds or thousand of degrees hotter than we are but our cold sources are at most a few dozen degrees colder. By his theory that’s why cold wave phenomena are masked by heat waves.”
“Give me a minute. … Ah, got it. The very meaning of a focal point is that all waves end or start there. A cold object at the sending station emits much less infrared than the warm object did. The thermoscope bulb now gets less than it emits. With less input from below its net energy drops. It chills.”
“Nice, Sy. Now for the other twist. Rumford published his theory in 1805. Herschel had already identified infrared radiation in the Sun’s spectrum in 1800. Two strikes against Herschel, I guess — he was British and he was an astronomer. Continental physicists wouldn’t bother to read his stuff.”
- Much of this material from Evans and Popp, American Journal of Physics. 53 (8): 737–753
~ Rich Olcott